How to log and view traces to LangSmith
LangSmith makes it easy to log and view traces from your LLM application, regardless of which language or framework you use.
Annotating your code for tracing
Using @traceable / traceable
LangSmith makes it easy to log traces with minimal changes to your existing code with the @traceable decorator in Python and traceable function in TypeScript.
The LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2 environment variable must be set to 'true' in order for traces to be logged to LangSmith, even when using @traceable or traceable. This allows you to toggle tracing on and off without changing your code.
Additionally, you will need to set the LANGCHAIN_API_KEY environment variable to your API key (see Setup for more information).
By default, the traces will be logged to a project named default.
To log traces to a different project, see this section.
- Python
- TypeScript
The @traceable decorator is a simple way to log traces from the LangSmith Python SDK. Simply decorate any function with @traceable.
from langsmith import traceable
from openai import Client
openai = Client()
@traceable
def format_prompt(subject):
return [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"What's a good name for a store that sells {subject}?"
}
]
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def invoke_llm(messages):
return openai.chat.completions.create(
messages=prompt, model="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0
)
@traceable
def parse_output(response):
return response.choices[0].message.content
@traceable
def run_pipeline():
messages = format_prompt("colorful socks")
response = invoke_llm(messages)
return parse_output(response)
run_pipeline()
The traceable function is a simple way to log traces from the LangSmith TypeScript SDK. Simply wrap any function with traceable.
Note that when wrapping a sync function with traceable, (e.g. formatPrompt in the example below), you should use the await keyword when calling it to ensure the trace is logged correctly.
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI();
const formatPrompt = traceable((subject: string) => {
return [
{
role: "system" as const,
content: "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
role: "user" as const,
content: `What's a good name for a store that sells ${subject}?`
}
];
}, { name: "formatPrompt" });
const invokeLLM = traceable(async (messages: { role: string; content: string }[]) => {
return openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: messages,
temperature: 0
});
}, { run_type: "llm", name: "invokeLLM" });
const parseOutput = traceable((response: any) => {
return response.choices[0].message.content;
}, { name: "parseOutput" });
const runPipeline = traceable(async () => {
const messages = await formatPrompt("colorful socks");
const response = await invokeLLM(messages);
return parseOutput(response);
}, { name: "runPipeline" });
await runPipeline()
Wrapping the OpenAI client
The wrap_openai/wrapOpenAI methods in Python/TypeScript allow you to wrap your OpenAI client in order to automatically log traces -- no decorator or function wrapping required!
The wrapper works seamlessly with the @traceable decorator or traceable function and you can use both in the same application.
The LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2 environment variable must be set to 'true' in order for traces to be logged to LangSmith, even when using wrap_openai or wrapOpenAI. This allows you to toggle tracing on and off without changing your code.
Additionally, you will need to set the LANGCHAIN_API_KEY environment variable to your API key (see Setup for more information).
By default, the traces will be logged to a project named default.
To log traces to a different project, see this section.
- Python
- TypeScript
import openai
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
@traceable(run_type="tool", name="Retrieve Context")
def my_tool(question: str) -> str:
return "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
@traceable(name="Chat Pipeline")
def chat_pipeline(question: str):
context = my_tool(question)
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": f"Question: {question}
Context: {context}"}
]
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages
)
return chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
chat_pipeline("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?")
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
const client = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const myTool = traceable(async (question: string) => {
return "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict.";
}, { name: "Retrieve Context", run_type: "tool" });
const chatPipeline = traceable(async (question: string) => {
const context = await myTool(question);
const messages = [
{
role: "system",
content:
"You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context.",
},
{ role: "user", content: `Question: ${question} Context: ${context}` },
];
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: messages,
});
return chatCompletion.choices[0].message.content;
}, { name: "Chat Pipeline" });
await chatPipeline("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?");
Using the RunTree API
Another, more explicit way to log traces to LangSmith is via the RunTree API. This API allows you more control over your tracing - you can manually
create runs and children runs to assemble your trace. You still need to set your LANGCHAIN_API_KEY, but LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2 is not
necessary for this method.
- Python
- TypeScript
import openai
from langsmith.run_trees import RunTree
# This can be a user input to your app
question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
# Create a top-level run
pipeline = RunTree(
name="Chat Pipeline",
run_type="chain",
inputs={"question": question}
)
await pipeline.post();
# This can be retrieved in a retrieval step
context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": f"Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"}
]
# Create a child run
child_llm_run = pipeline.create_child(
name="OpenAI Call",
run_type="llm",
inputs={"messages": messages},
)
# Generate a completion
client = openai.Client()
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages
)
# End the runs and log them
child_llm_run.end(outputs=chat_completion)
child_llm_run.post()
pipeline.end(outputs={"answer": chat_completion.choices[0].message.content})
pipeline.post()
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { RunTree } from "langsmith";
// This can be a user input to your app
const question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?";
const pipeline = new RunTree({
name: "Chat Pipeline",
run_type: "chain",
inputs: { question }
});
// This can be retrieved in a retrieval step
const context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict.";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ role: "user", content: `Question: ${question}
Context: ${context}` }
];
// Create a child run
const childRun = await pipeline.createChild({
name: "OpenAI Call",
run_type: "llm",
inputs: { messages },
});
// Generate a completion
const client = new OpenAI();
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: messages,
});
// End the runs and log them
childRun.end(chatCompletion);
await childRun.postRun();
await pipeline.end({ outputs: { answer: chatCompletion.choices[0].message.content } });
await pipeline.patchRun();
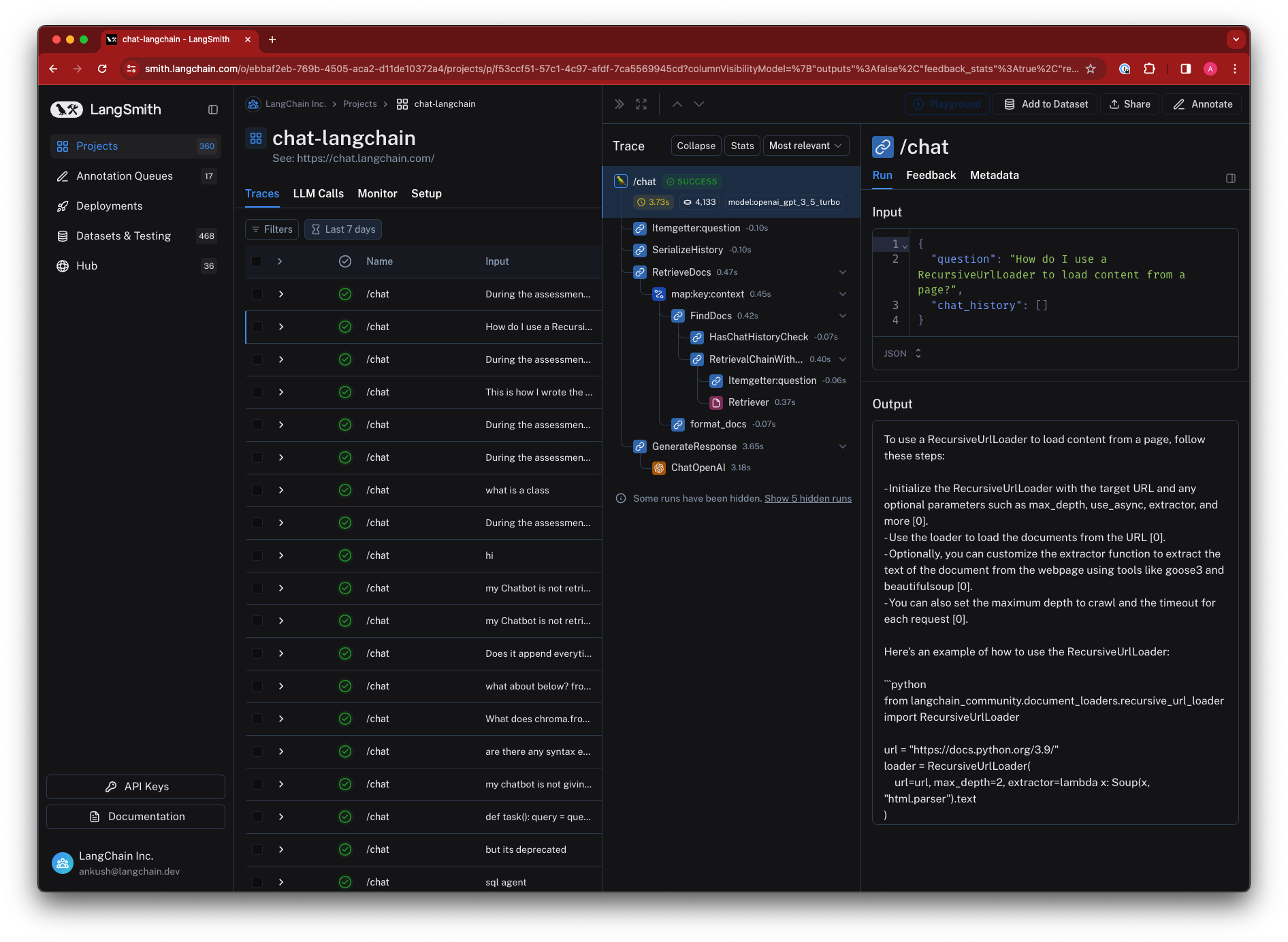
Viewing Traces
To view traces, navigate to the project details page for your project (by default, all traces are logged to the "default" project).
Then, click on a row in the traces table to expand the trace. This will bring up a run tree, which shows the parent-child relationships between runs, as well as the inputs and outputs of each run.
You can also view feedback, metadata, and other information in the tabs.
Setting a sampling rate for tracing
To downsample the number of traces logged to LangSmith, set the LANGCHAIN_TRACING_SAMPLING_RATE environment variable to
any float between 0 (no traces) and 1 (all traces). This requires a python SDK version >= 0.0.84, and a JS SDK version >= 0.0.64.
For instance, setting the following environment variable will filter out 25% of traces:
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_SAMPLING_RATE=0.75
This works for the traceable decorator and RunTree objects.
Distributed Tracing
LangSmith supports distributed tracing out of the box, linking runs within a trace across services using context propagation headers (langsmith-trace and optional baggage for metadata/tags).
Example client-server setup:
- Trace starts on client
- Continues on server
# client.py
from langsmith.run_helpers import get_current_run_tree, traceable
import httpx
@traceable
async def my_client_function():
headers = {}
async with httpx.AsyncClient(base_url="...") as client:
if run_tree := get_current_run_tree():
# add langsmith-id to headers
headers.update(run_tree.to_headers())
return await client.post("/my-route", headers=headers)
Then the server (or other service) can continue the trace by passing the headers in as langsmith_extra:
# server.py
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.run_helpers import tracing_context
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
@traceable
async def my_application():
...
app = FastAPI() # Or Flask, Django, or any other framework
@app.post("/my-route")
async def fake_route(request: Request):
# request.headers: {"langsmith-trace": "..."}
# as well as optional metadata/tags in `baggage`
with tracing_context(parent=request.headers):
return await my_application()
The example above uses the tracing_context context manager. You can also directly specify the parent run context in the trace context manager or traceable decorator.
from langsmith.run_helpers import traceable, trace
# ... same as above
@app.post("/my-route")
async def fake_route(request: Request):
# request.headers: {"langsmith-trace": "..."}
# as well as optional metadata/tags in `baggage`
my_application(langsmith_extra={"parent": request.headers})
# Or using the `trace` context manager
with trace(parent=request.headers) as run_tree:
...
run_tree.end(outputs={"answer": "42"})
...
Turning off tracing
If you've decided you no longer want to trace your runs, you can remove the environment variables configured to start tracing in the first place.
By unsetting the LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2 environment variable, traces will no longer be logged to LangSmith.
Note that this currently does not affect the RunTree objects.
This setting works both with LangChain and the LangSmith SDK, in both Python and TypeScript.
Getting the run ID of a logged run
The example below shows how to get the run ID of a logged run using the LangSmith SDK. To get the run ID of a run using LangChain, you can follow the guide here.
- Python
- TypeScript
- API (Using Python Requests)
import openai
from uuid import uuid4
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.run_trees import RunTree
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": "Is sunshine good for you?" }
]
# Collect run ID using RunTree
run_id = uuid4()
rt = RunTree(
name="OpenAI Call RunTree",
run_type="llm",
inputs={"messages": messages},
id=run_id
)
client = openai.Client()
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages
)
rt.end(outputs=chat_completion)
rt.post()
print("RunTree Run ID: ", run_id)
# Collect run ID using openai_wrapper
run_id = uuid4()
client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages, langsmith_extra={
"run_id": run_id,
},
)
print("OpenAI Wrapper Run ID: ", run_id)
# Collect run id using traceable decorator
run_id = uuid4()
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
name="OpenAI Call Decorator",
)
def call_openai(
messages: list[dict], model: str = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
) -> str:
return client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
).choices[0].message.content
result = call_openai(
messages,
langsmith_extra={
"run_id": run_id,
},
)
print("Traceable Run ID: ", run_id)
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { RunTree } from "langsmith";
import {v4 as uuidv4} from "uuid";
const client = new OpenAI();
const messages = [
{role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant."},
{role: "user", content: "Is sunshine food for you?"}
];
const runId = uuidv4();
const rt = new RunTree({
run_type: "llm",
name: "OpenAI Call RunTree",
inputs: { messages },
id: runId
})
await rt.postRun();
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages: messages,
});
rt.end(chatCompletion)
await rt.patchRun()
console.log("Run ID: ", runId);
import openai
import requests
from datetime import datetime
from uuid import uuid4
# Send your API Key in the request headers
headers = {
"x-api-key": "ls__..."
}
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": "Is sunshine good for you?" }
]
start_time = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
client = openai.Client()
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo", messages=messages
)
run_id = uuid4()
requests.post(
"https://api.smith.langchain.com/runs",
json={
"id": run_id.hex,
"name": "OpenAI Call",
"run_type": "llm",
"inputs": {"messages": messages},
"start_time": start_time,
"outputs": {"answer": chat_completion.choices[0].message.content},
"end_time": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
},
headers=headers
)
print("API Run ID: ", run_id)
Getting the URL of a logged run
Runs are logged to whichever project you have configured ("default" if none is set), and you can view them by opening the corresponding project details page. To programmatically access the run's URL, you can use the LangSmith client. Below is an example. To get the run ID of a run, you can follow the guide here.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
run = client.read_run("<run_id>")
print(run.url)
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const client = new Client();
const runUrl = await client.getRunUrl({runId: "<run_id>"});
console.log(runUrl);
Deleting traces in a project
You can delete a project, along with all its associated traces and other information, in the UI or by using the LangSmith client.
Below is an example using the SDK:
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
client.delete_project(project_name="<project_name>")
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const client = new Client();
await client.deleteProject({projectName: "<project_name>"});