How to use prebuilt evaluators
LangSmith integrates with the open-source openevals package
to provide a suite of prebuilt evaluators that you can use as starting points for evaluation.
This how-to guide will demonstrate how to set up and run one type of evaluator (LLM-as-a-judge). For a complete list of prebuilt evaluators with usage examples, refer to the openevals and agentevals repos.
Setup
You'll need to install the openevals package to use the pre-built LLM-as-a-judge evaluator.
- Python
- TypeScript
pip install -U openevals
yarn add openevals @langchain/core
You'll also need to set your OpenAI API key as an environment variable, though you can choose different providers too:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your_openai_api_key"
We'll also use LangSmith's pytest integration for Python and Vitest/Jest for TypeScript to run our evals.
openevals also integrates seamlessly with the evaluate method as well.
See the appropriate guides for setup instructions.
Running an evaluator
The general flow is simple: import the evaluator or factory function from openevals, then run it within your
test file with inputs, outputs, and reference outputs. LangSmith will automatically log the evaluator's results as feedback.
Note that not all evaluators will require each parameter (the exact match evaluator only requires outputs and reference outputs, for example). Additionally, if your LLM-as-a-judge prompt requires additional variables, passing them in as kwargs will format them into the prompt.
Set up your test file like this:
- Python
- TypeScript
import pytest
from langsmith import testing as t
from openevals.llm import create_llm_as_judge
from openevals.prompts import CORRECTNESS_PROMPT
correctness_evaluator = create_llm_as_judge(
prompt=CORRECTNESS_PROMPT,
feedback_key="correctness",
model="openai:o3-mini",
)
# Mock standin for your application
def my_llm_app(inputs: dict) -> str:
return "Doodads have increased in price by 10% in the past year."
@pytest.mark.langsmith
def test_correctness():
inputs = "How much has the price of doodads changed in the past year?"
reference_outputs = "The price of doodads has decreased by 50% in the past year."
outputs = my_llm_app(inputs)
t.log_inputs({"question": inputs})
t.log_outputs({"answer": outputs})
t.log_reference_outputs({"answer": reference_outputs})
correctness_evaluator(
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
reference_outputs=reference_outputs
)
import * as ls from "langsmith/vitest";
// import * as ls from "langsmith/jest";
import { createLLMAsJudge, CORRECTNESS_PROMPT } from "openevals";
const correctnessEvaluator = createLLMAsJudge({
prompt: CORRECTNESS_PROMPT,
feedbackKey: "correctness",
model: "openai:o3-mini",
});
// Mock standin for your application
const myLLMApp = async (_inputs: Record<string, unknown>) => {
return "Doodads have increased in price by 10% in the past year.";
}
ls.describe("Correctness", () => {
ls.test("incorrect answer", {
inputs: {
question: "How much has the price of doodads changed in the past year?"
},
referenceOutputs: {
answer: "The price of doodads has decreased by 50% in the past year."
}
}, async ({ inputs, referenceOutputs }) => {
const outputs = await myLLMApp(inputs);
ls.logOutputs({ answer: outputs });
await correctnessEvaluator({
inputs,
outputs,
referenceOutputs,
});
});
});
The feedback_key/feedbackKey parameter will be used as the name of the feedback in your experiment.
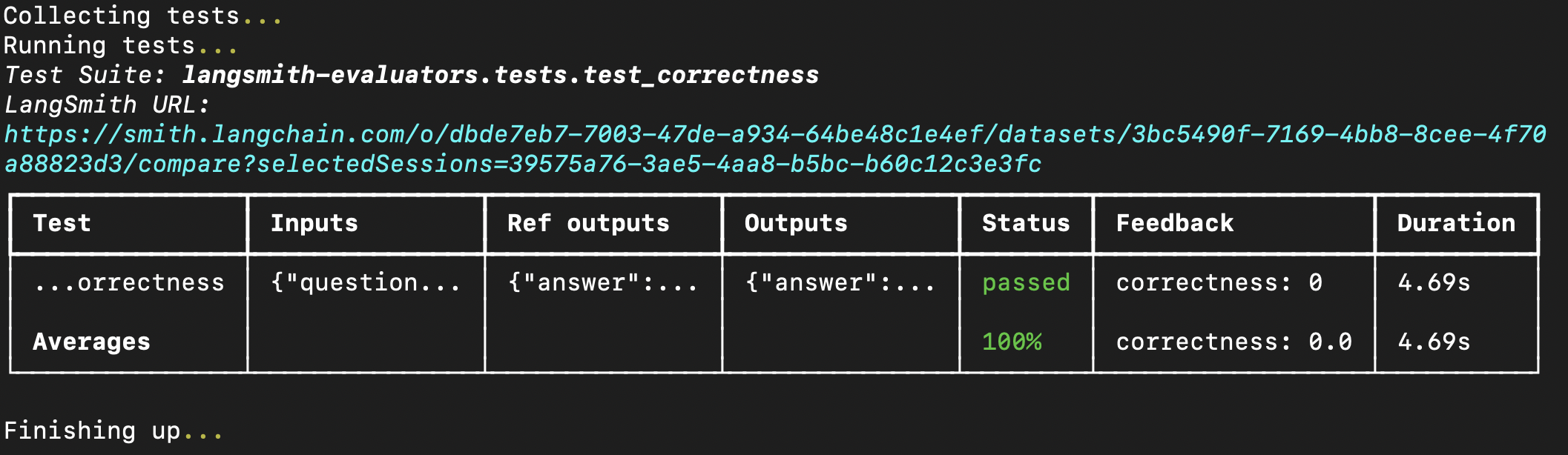
Running the eval in your terminal will result in something like the following:
You can also pass prebuilt evaluators directly into the evaluate method if you have already created a dataset in LangSmith.
If using Python, this requires langsmith>=0.3.11:
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import Client
from openevals.llm import create_llm_as_judge
from openevals.prompts import CONCISENESS_PROMPT
client = Client()
conciseness_evaluator = create_llm_as_judge(
prompt=CONCISENESS_PROMPT,
feedback_key="conciseness",
model="openai:o3-mini",
)
experiment_results = client.evaluate(
# This is a dummy target function, replace with your actual LLM-based system
lambda inputs: "What color is the sky?",
data="Sample dataset",
evaluators=[
conciseness_evaluator
]
)
import { evaluate } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { createLLMAsJudge, CONCISENESS_PROMPT } from "openevals";
const concisenessEvaluator = createLLMAsJudge({
prompt: CONCISENESS_PROMPT,
feedbackKey: "conciseness",
model: "openai:o3-mini",
});
await evaluate(
(inputs) => "What color is the sky?",
{
data: datasetName,
evaluators: [concisenessEvaluator],
}
);
For a complete list of available evaluators, see the openevals and agentevals repos.